What Is The Function Of The Cytoplasm In An Animal Cell
Brief History of Cytoplasm
In the year 1665, Robert Hooke, an English researcher observed the fundamental unit of measurement of life through his fibroid compound microscope. He coined the term "cell", which was based on the Latin word chosen "Cella," meaning, small rooms.
Later, many scientists contributed to Robert Hooke'south findings and somewhen, the Cell Theory was postulated. As engineering science progressed, modern interpretations of Jail cell Theory accept been formed, with new tenets and revisions of the existing ones.
In 1863, a Swiss biologist named Rudolf von Kölliker coined the term "Cytoplasm," just it was regarded as a synonym for protoplasm. However, the term gradually changed its meaning to the electric current definition of the term "cytoplasm".
Table of Contents
- Explanation
- Diagram
- Construction
- Part
- Protoplasm
- Nucleus
What is Cytoplasm?
The fluid that fills up the cells is referred to as the cytoplasm. It encompasses the cytosol with filaments, ions, proteins, and macromolecular structures and also other organelles suspended in the cytosol.
But new research suggests that the traditional definition of cytoplasm is no longer valid. Decades prior, it was considered to be a fluid-like substance, merely new evidence reveals that information technology is similar to drinking glass-forming liquids.
The cytoplasm in the eukaryotic cells assembly with the prison cell contents except for the nucleus. But in prokaryotic cells, as they do not possess a defined nuclear membrane, the cytoplasm possesses the genetic material of the cell. The cells, in comparing to the eukaryotes, are smaller and accept an unproblematic arrangement of the cytoplasm.
Also Read:Deviation between Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis
Cytoplasm Diagram
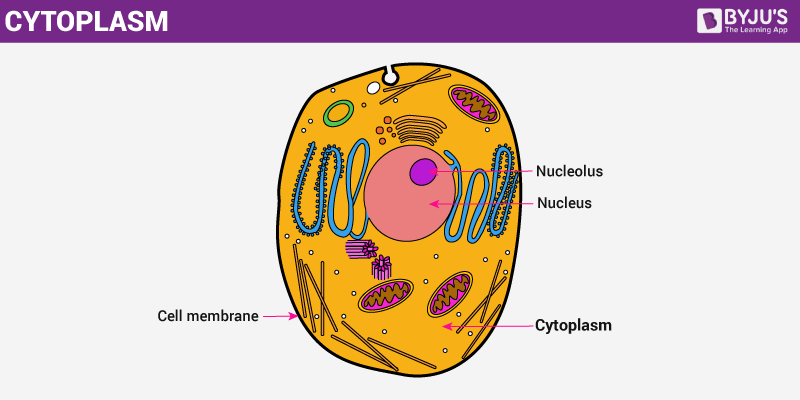
The cytoplasm is a fluid-similar substance that fills up the cells. Cellular organelles and structures are suspended in the cytoplasm.
Cytoplasm Structure
Cell organelles are diverse structures existing inside cells. All these structures are distinct and perform specific functions. Cells accept three main elements i.due east., plasma membrane, and cytoplasm and the nucleus.
The plasma membrane or cell membrane is a bi-lipid bleary layer, parting the jail cell organelles from its exterior environment and from the different cells. It is the external covering of a cell where all different parts, including cytoplasm and nucleus, are enclosed.
Next, is the nucleus, ane of the biggest organelle. They have exclusive control of a jail cell. Lastly, the cytoplasm is a jelly-like material in which the cell organelles are implanted.
The cytoplasm is an essential component of the cell. It is a semi-liquid jelly-like cloth, which joins the nucleus and the cell membrane. In the cell, the cytoplasm is embedded, while other cell organellessuch as endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, ribosomes, vacuoles, etc. are all suspended within it.
It tin can easily exist examined under a microscope through the staining technique. Functionally, it is the site for several chemical reactions within a prison cell. Well-nigh of the cellular metabolism takes place here.
Also Refer: Deviation between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Cytoplasm Part
One of the major functions of cytoplasm is to enable cells to maintain their turgidity, which enables the cells to agree their shape. Other functions of cytoplasm are every bit follows:
- The jelly-like fluid of the cytoplasm is composed of common salt and water and is present within the membrane of the cells and embeds all of the parts of the cells and organelles.
- The cytoplasm is home to many activities of the cell as it contains molecules, enzymes that are crucial in the pause down of the waste.
- The cytoplasm also assists in metabolic activities.
- Cytoplasm provides shape to the jail cell. It fills up the cells thus enabling the organelles to remain in their position. The cells, without cytoplasm, would deflate and substances will non permeate hands from one to the other organelle.
- A function of the cytoplasm, the cytosol has no organelles. Rather, the cytosol is enclosed by matrix boundaries that fill up the prison cell section which does not agree the organelles.
The whole cellular content of a living prison cell is called protoplasm. The cytoplasm, nucleus and all other living components of the cell together make up the protoplasm of a cell.
Further Reading: Difference Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm
Protoplasm
The protoplasm is generally referred to every bit the living part of the cell. It is the colourless, jelly-like substance composed of macromolecules, water and mixture of small molecules. It can be defined every bit the inorganic and organic substance which constitutes the cytoplasm, the nucleus, mitochondria and the plastids of the cell. It is the chief substance that is responsible for all the living processes.
The primary component of the protoplasm is the cytoplasm which is situated between the nucleus and the cell membrane in the eukaryotic cells. It contains all the organelles. Information technology regulates the environment of the cell and maintains the cell shape. Information technology stores the substances and chemicals that are necessary for the organelle.
The second component of the protoplasm is the nucleus, which contains the genetic material of an organism and is situated in the nucleus. The nucleus contains the ribosomes that are required and are crucial for the protein synthesis in the cells.
Merely in the case of prokaryotes, the nucleoid is present in identify of the nucleus, wherein all the genetic information is present. Notwithstanding, it does not have a nuclear membrane; hence, the term protoplasm does not apply.
The elements that brand up the protoplasm are fats, proteins, enzymes, hormones, etc. which are either suspended or dissolved in the fluid component of the protoplasm.
Besides Read:Protoplasm
Nucleus
The nucleus is an of import chemical element of the cells. It is a membrane-spring organelle that is typically found in the eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, whereas some cell types practice not possess a nucleus (RBC-Red Blood Cells).
Also Refer:Cytoskeleton
Learn more in detail about the cytoplasm, its construction, functions, other cell organelles and other related topics at BYJU'S Biology
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is the fluid present in the cell enclosed inside the cell membrane that comprises water and enzymes, salts, and various organelles.
What is the of import function of cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is responsible for holding the components of the cell and protects them from damage. It stores the molecules required for cellular processes and is likewise responsible for giving the prison cell its shape.
What would happen if the cell had no cytoplasm?
A cell would be deflated and flat and would not be able to retain its shape without the cytoplasm. The organelles will not be able to suspend in the cell.
What would happen if there was no nucleus in the cell?
The nucleus contains the hereditary textile and is responsible for cell division. It is known as the brain of the cell and controls all its activities. Without a nucleus, the cell volition not be able to perform whatever activity and volition eventually die. There will be no replication and no synthesis of proteins.
What is the charge in the cytoplasm?
For every single ATP molecule, 3 sodium ions are exported to the extracellular space of the cell while ii potassium ions are imported to the cytoplasm. Thus the cytoplasm is negatively charged.
What is the pH of cytoplasm?
The pH of the cytoplasm is vii.four.
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/cytoplasm-structure-function/
Posted by: maloneruty2001.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Is The Function Of The Cytoplasm In An Animal Cell"
Post a Comment